The Smart Marketer’s Guide to Accurate Lead Scoring
If you ask most sales and marketing teams what their ultimate goal is, you can pretty much guarantee that they will say it is generating more leads and conversions. And many of them make the mistake of keeping their primary focus on the top of the sales funnel. After all, if you have more leads coming in, then you’ll have more conversions too, right?
Well, of course, this is not always necessarily the case. Sometimes your leads are weak and they don’t have the necessary intent to use your product or a need that it can solve.
This is why a good lead scoring system is so important. It can save marketing and sales teams lots of time and ensure that their efforts make a greater impact.
Businesses that have implemented lead scoring attest to it driving higher rates for the following:
- Sales productivity – helping your sales team personalize their sales pitch to customers
- Conversions – as you learn to prioritize quality leads over cold leads in your marketing activities
- Alignment of marketing and sales – as both departments are given the opportunity to make well-informed decisions based on gathered data
Quick Takeaways:
- By only pursuing leads that are likely going to convert, all of your marketing moves with be more strategic and effective.
- Build your lead scoring model carefully. Know its strong and weak points.
- Take into account the demographics, interests, and previous behavior of every customer segment and cohort. Build your buyer personas accordingly.
- Tweak your lead scoring and qualification process to suit your buyer’s journey and marketing approach.
What Is Lead Scoring?
Lead scoring is a business process used by B2B companies for the purpose of automating the prioritizing, ranking, grouping, routing and tracking of leads that are interacting with and responding to marketing or sales campaigns.
Over the last few years, lead scoring has become more important for companies who are engaging in a moderate to large amount of online marketing activities. Lead scoring is typically offered as an integral module within a marketing automation platform (MAP). It’s designed to ensure your company has a consistent process for the management of leads as they move through the sales funnel to the opportunity stage.
Metrics & Data You Can Use for Lead Scoring
Website Activity
Website activity can be broken into general attributes – time on site, and specific attributes – downloaded particular asset on pricing page. You can identify website activity per individual by capturing a first party cookie placed on their computer via web tracking software provided by the MAP. A website visitor is typically cookied as a result of clicking through a link in an email campaign or visiting the website.
Campaign Responses
Scoring campaign responses means having the ability to score on an email campaign open or click and a form or landing page completion. Campaign response scoring may target general attributes – opened any email campaign, or score on the general attribute – completed any form, or on a specific response to a specific question in a special form. Having a combination of general and specific response attribute values will increase the accuracy of the scoring model and allow you to improve routing rules.
Demographics and Firmographics
These two terms are essentially the same: they are data points that reveal the attributes of individuals and firms that marketers use to define their target market. B2B marketers should be looking at all basic data such as the nature of business, the number of employees, and profit, as well as IAO (interests, attitudes, and opinions) variables. Some of the key demographics and firmographics that should be gathered for the sales team include:
- Title
- Business size and industry
- Location
- Department
Behavioral Data
Customers’ online and offline activities are great indicators of their interest in your brand and their readiness to buy. Things that you can look at include behavior on your website, email engagement, eBooks downloaded, and forms submitted.
You should talk to your customers and your sales teams to determine which of these metrics matter most.
Input from Sales and Customer Service
Your sales and customer service departments are your company’s front lines. By having direct interactions and communication with customers, they can become a valuable source of insights into what your customers think of or expect from your brand, helping you develop more effective strategies in the future.
Criteria Setting
To develop a good lead scoring campaign, you first need to determine the criteria for assigning values that will gauge the quality of your leads. The criteria you set will ultimately guide you in tracking and following up on your prospects, helping you filter out those that are more or less likely to convert.
You can use the BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, and Timeline) model as your set of criteria for ranking your leads. Under this model, you’ll need to assess your prospects in terms of:
- Budget: The budget may pertain to the actual spending allotment that companies set. Your criteria should cover the measurable gains for individuals or organizations as they stand to benefit from your products or services, whether it be in the form of decreased costs or increased efficiency in their processes.
- Authority: The same principle applies to identifying which prospects in a company qualify when it comes to having the authority to make purchasing decisions. You should not only be targeting those with defined purchasing powers but also those who are capable of promoting your brand to their peers (influencers) and those who act as “information gatekeepers” to the rest of the organization.
- Need: The idea here is that you’re offering something valuable that customers can use to solve their problems. You don’t want to target audiences that aren’t relevant. For example, if your business sells office supplies, you’ll probably want to avoid targeting home-businesses, as they’re unlikely to make large office supply purchases on a regular basis.
- Timing: Here, you must factor in the entire buying cycle of your customers. Some customers have a predetermined timeline for making purchases. But be careful not to disregard those who might not necessarily be in-market to buy. Use that window of opportunity to educate your prospects about your products and services until they define their need and are ready to place an order with you.
How to Build a Lead Scoring Model
Essentially, lead scoring can help you determine the quality of your leads by ranking them according to their sales potential. The leads who show more interest in your product/service offering and those who fit your ideal buyer persona will end up getting the highest scores.
Here’s a video from Emarketer to get you started on the finer points of lead scoring:
In the most basic terms, lead scoring involves assigning a value (typical “points”) to various factors that signal the likelihood that a consumer will convert. These variables are based on internal behavioral data that has been gathered from tracking individual customer accounts and monitoring how they’ve engaged with your business.
If a customer has more interactions, such as creating an online account, clicking on a promotional ad, and engaging with blog content, we assume that they have a greater propensity to use our product or bent towards our brand, and consequently we assign them a higher lead score.
Every interaction will have a different point value assigned to it based on how influential it is on customer conversions. For example, if a customer reaches out to the sales department, they are much more likely to convert. Other actions like engaging with a post on social media or opening a marketing email will have a lower point value because they are not necessarily strong signals that imply conversion.
While this sounds fairly easy to implement, the truth is that there’s a lot of effort involved, which is why the majority of businesses aren’t doing it. Not scoring your leads, however, can severely cut into profit margins and slow down the sales cycle if marketing and sales teams focus on engaging and converting leads that are irrelevant or uninterested. Data from our studies show that businesses that create an effective lead nurturing program are able to cut costs by 33% and increase conversions by 50%.
Everyone should understand the rationale behind the scoring model so they can accept the higher-value leads once they begin to flow into the CRM. Marketing should show sales elements such as assets and pages on the website. And sales should provide insight into what they think is high, medium and low value.
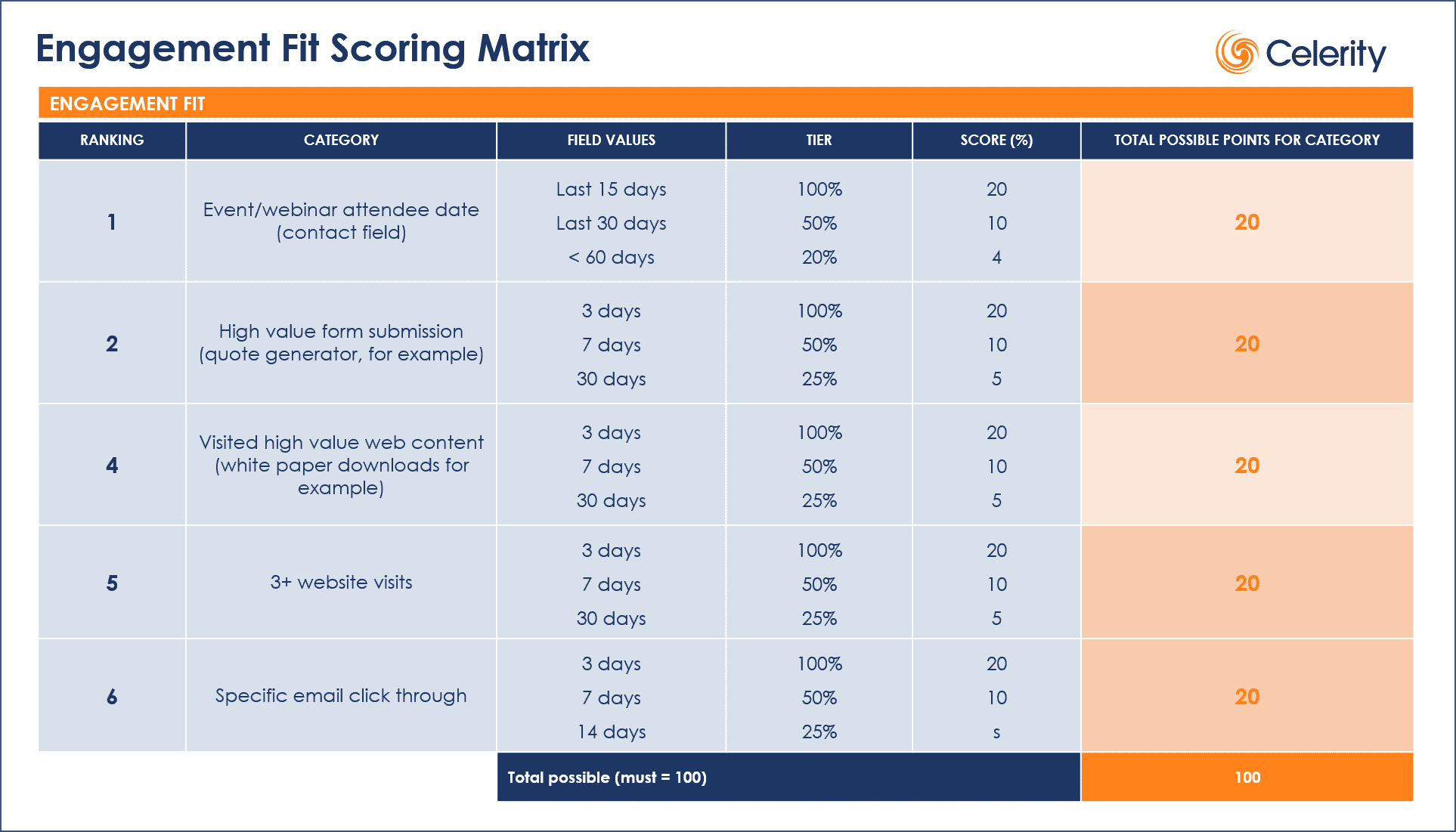
There are four key steps to follow when establishing the values of each score-able action:
- Creating Scoring Groups: Upon completion and mutual approval of the actions and associated values determined by sales and marketing, the scoring groups can be created. A scoring group is a group of leads who have achieved the same scored value rage – typically +/- a certain number of points, depending on how sales and marketing teams craft the values.
- Creating Scoring Actions: Once the scoring groups are created, it’s time to create the scoring actions and routing rules. There should be an established process for lead follow-up between sales and marketing. For example, once a “hot” lead is passed from marketing, it should be understood by the sales team that it’s now their responsibility to follow up. We suggest setting up a meeting between the two teams to map out the rules and actions that the company will take against leads when they score into or out of a particular group.
- Creating the Feedback Loop: Placing the lead scoring name in a database field inside of the lead entities is critical. This step allows marketing to pull periodic reports on the health of the lead scoring model based upon the lead status disposition changes for “hot” leads passed to CRM. The report should show that if X amount of hot leads were passed to the CRM, a decent percentage of these leads should continue moving forward to the sales cycle. Feedback loop reporting acts as a validation of the established lead scoring rule for marketing and sales.
- Testing and Adjusting: A new lead scoring model should be tested for a period of approximately 90 days. Continuous communication between marketing and sales during the initial release period for the lead scoring model will help both teams make the necessary adjustments and ensure the lead scoring model is accurate.
So, how do we put customers in the proper brackets according to their purchase intent?
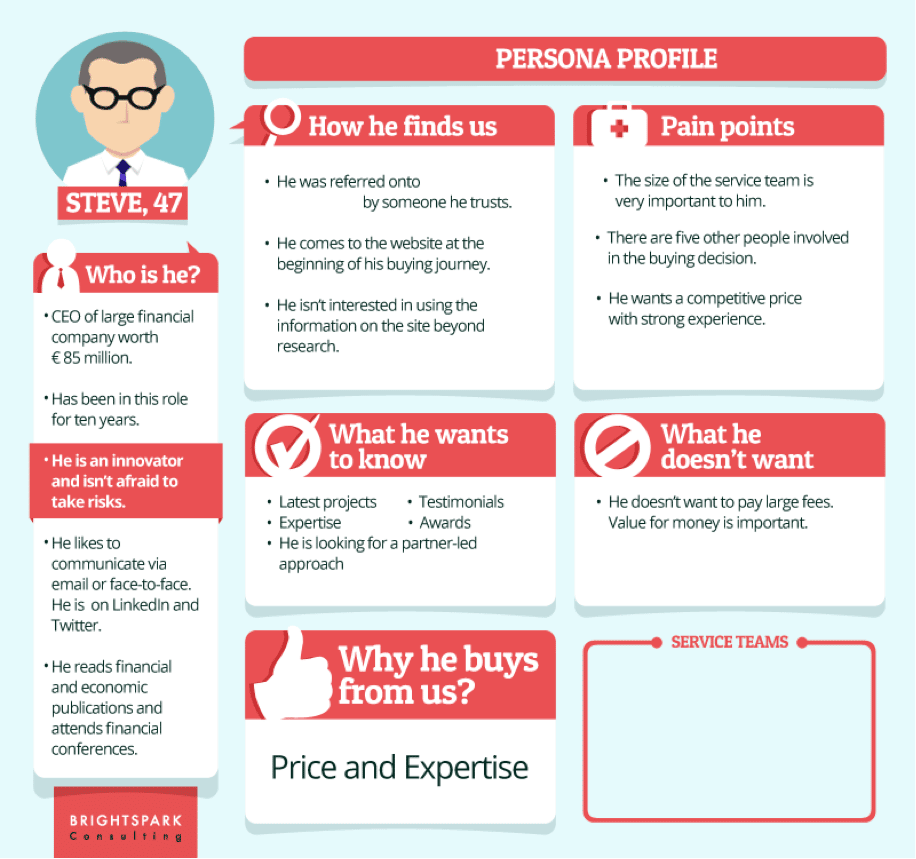
Creating Buyer Personas and Accurate Segments
The key to lead scoring is understanding who your “best” customers are and which ones have the highest chances of converting. The optimal way to do this is by creating personas supported by accurate data. Since this approach to lead nurturing is so personalized, your team will benefit the most from using a research-based ABM (Account-Based Marketing) program – it lets your team follow every customer’s individual journey, and determine whether or not (and how) each interaction correlates with a conversion.
ABM also makes it far easier to create a properly segmented audience that your team can target and nurture. Say your business’s audience is made up of 35% C-level business professionals, 55% small business owners, and 10% that fit into other categories. Such information can help you to create separate brand personas that highlight the preferences and priorities that each of these segments tends to have.
Furthermore, you can use behavioral data that has been collected with an ABM program to see the kind of content or interactions that influence each persona the most. This will be helpful for establishing a good lead scoring system because it shows which types of customers have the highest chance of conversions and deserve more attention when it comes to lead nurturing.
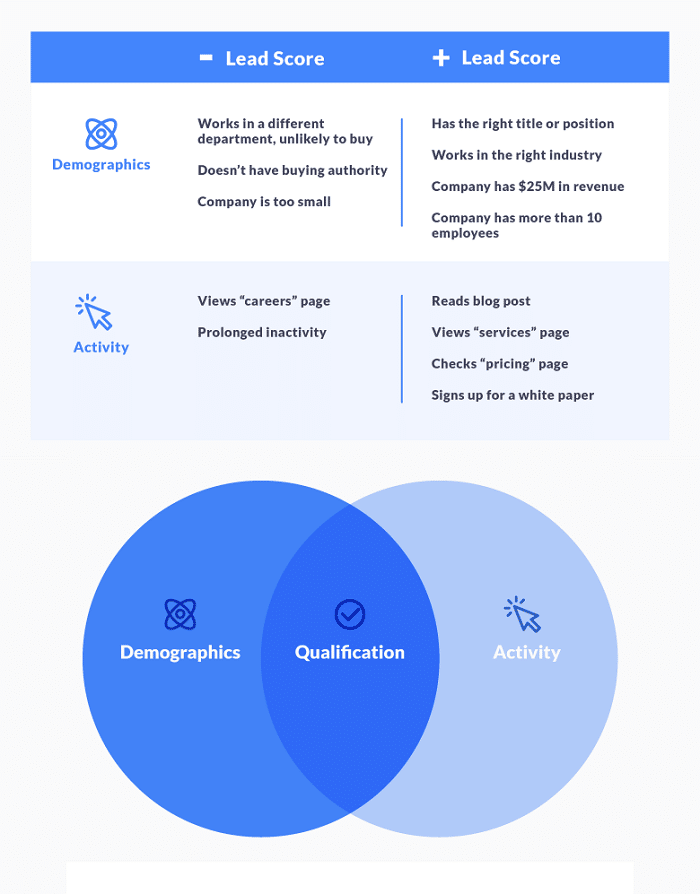
Scoring on the Basis of Demographic and Behavioral Criteria
Once you have this clearer understanding of your audience makeup, you can start to categorize the criteria for lead scoring. Take a look at the consumer data that you have gathered from past sales and leads. Start off with some of the descriptive demographic factors that your converted customers share in common.
Do the majority of your converted consumers fit into a similar age group, location, or job title? For B2C entities, what household income bracket is most interested? For B2B, how large are the majority of the companies that you service? What industries are more likely to buy from you?
As you identify these criteria, you can think about a score that is proportional to the value that each of them bring to the conversion, and how will you turn these into weights to assign to future leads.
Next, you should focus on behavioral data that signals potential conversions. Look at your data and pinpoint the behaviors that lead to micro-conversions like email link clicks, newsletter subscriptions, free trial requests, content downloads, or webinar viewers. Take a look at the conversion rates for each of these factors and score accordingly, allocating more points to the ones that are more likely to convert.
Key Questions to Answer Before Implementing Lead Scoring
When developing a lead scoring model, just be sure you can answer these 10 questions below. Doing so will dramatically improve the process of establishing a model and the overall lead-to-revenue cycle in your company.
- What are the score-able attributes captured?
- Who owns the leads coring model?
- How many scoring groups will we monitor?
- What are the scoring actions we will take against these groups?
- How will we validate and measure the scoring model?
- How will we validate and measure the scoring models?
- How should sales be alerted when a lead scores high?
- Have marketing and sales agreed on all aspects of the model?
- How should we display scoring data in CRM?
- Should scores degrade over time due to lack of activity?
Sales-Marketing Alignment on Lead Scoring
The point of a lead scoring system is to help marketers and salespeople optimize their efforts by focusing on accounts that have the highest chances of converting – but they should also be making it easier for more leads to interact with the content that influences them.
For example, if your product ads on Google or Facebook are not driving engagement or valuable leads, but your website blog content is highly influential and considered authoritative in your industry, then perhaps you should focus on getting more visibility for your content, channeling customers to your landing pages via your blog, and re-evaluating your advertising or PPC strategies.
In many companies, sales collaborates with marketing to define the elements of the scoring model and help establish the relative point values of actions and activities. From here, marketing usually takes full ownership of the lead scoring model. They can control whether a lead goes to sales or stays within the control of marketing (i.e. gets put into a separate nurture program).
Tweaking Your Lead Scoring and Conversion Process
A smart lead scoring, grading, and qualifying process can be a total game-changer for your company in terms of conversions. However, your model needs to be founded on data in order for it to be accurate and useful.
There are several key ingredients that you need to create an effective lead scoring system:
- A marketing process that records and categorizes important consumer data
- Data-based audience segmentation with specific personas
- A scoring system that takes into account both demographic and behavioral factors
- Close sales-marketing alignment with a focus on conversions
When these things fall into place, you can expect to see more results for marketing efforts, better audience engagement, and shorter sales cycles. That’s a sure sign that your bottom line is going to climb up!
What attributes do you base your lead scores on? What weightage do you assign them? How do you define MQLs and SQLs? How do you go after your most valuable prospects? Care to share in the comments?
Do you want to use some of the marketing strategies seen here or need more advice? Marketing Insider Group can produce conversion-focused web content for your business. Check out our weekly blog content service or schedule a free consultation.